Output Devices
Objectives of the week
- Measure the power consumption of an output device.
- Understand basic concept of voltage ,current and power.
- Calculation of power by measuring voltage and current.
- Understand output devices.
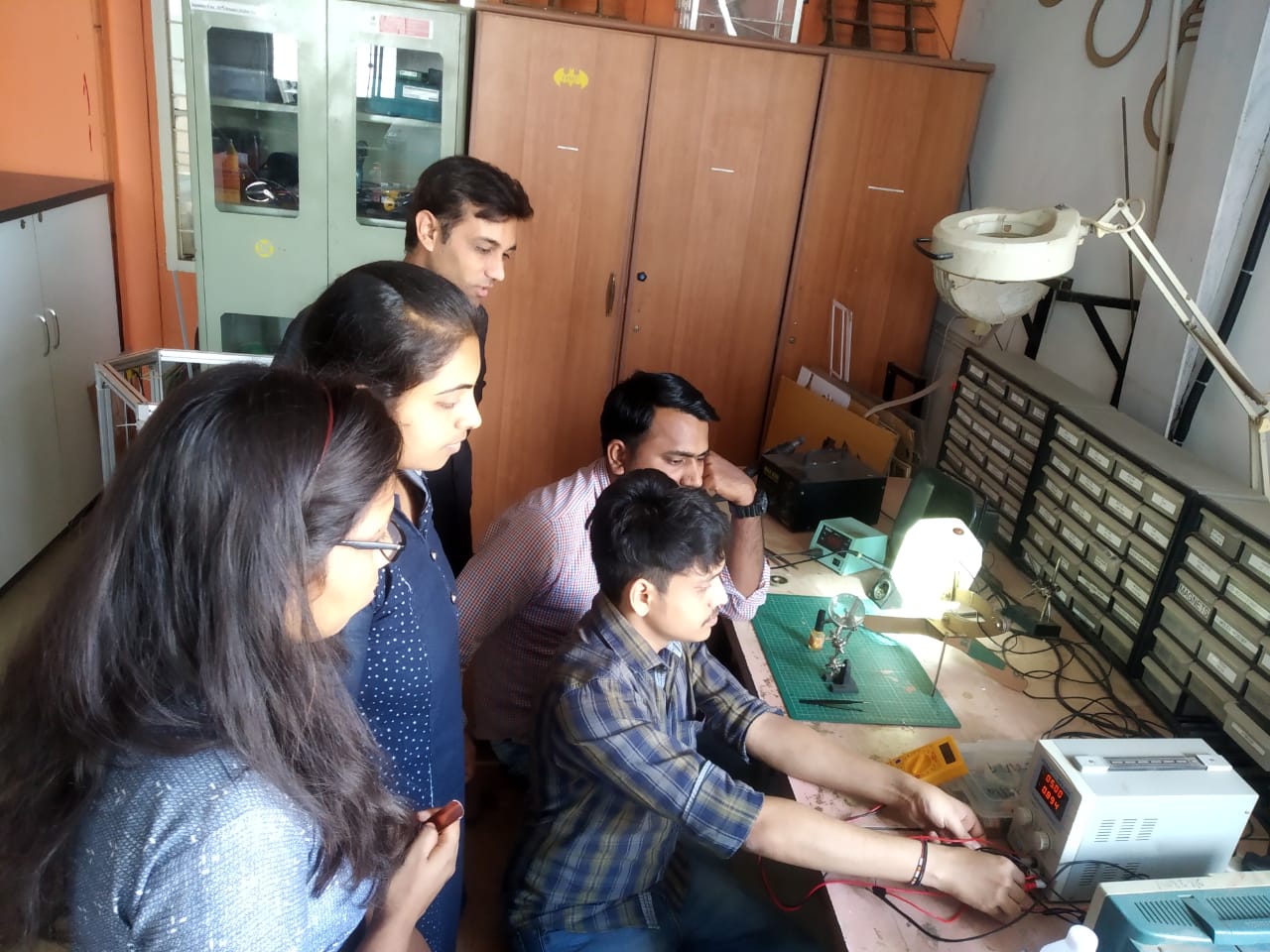
1. Group assignment
Learning outcome
In this week we have to calculate power of output devices .For that we need to calculate voltage and current of output device.First lets understand about voltage and current.
Voltage:
Voltage, electric potential difference, electric pressure or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points. The difference in electric potential between two points (i.e., voltage) in a static electric field is defined as the work needed per unit of charge to move a test charge between the two points. In the International System of Units, the derived unit for voltage is named volt. In SI units, work per unit charge is expressed as joules per coulomb, where 1 volt = 1 joule (of work) per 1 coulomb (of charge). The official SI definition for volt uses power and current, where 1 volt = 1 watt (of power) per 1 ampere (of current).
We calculated voltage of LCD display.For this assignment we used vikram sir's output board.We chacked voltage of LCD using multimeter.
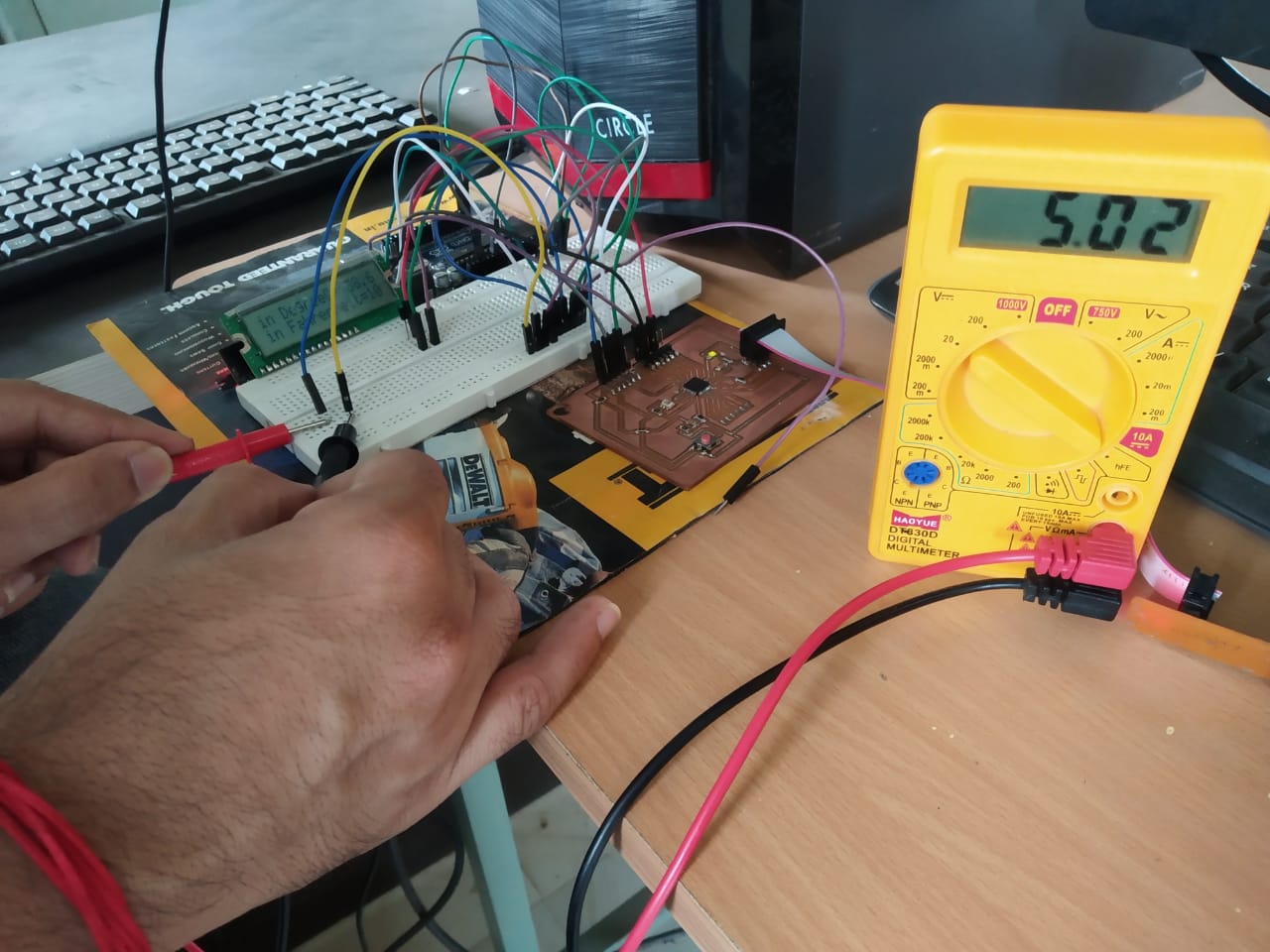
Current:
An electric current is the rate of flow of electric charge past a point or region. An electric current is said to exist when there is a net flow of electric charge through a region.In electric circuits this charge is often carried by electrons moving through a wire. It can also be carried by ions in an electrolyte, or by both ions and electrons such as in an ionized gas (plasma).
The SI unit of electric current is the ampere, which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. The ampere (symbol: A) is an SI base unit. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter
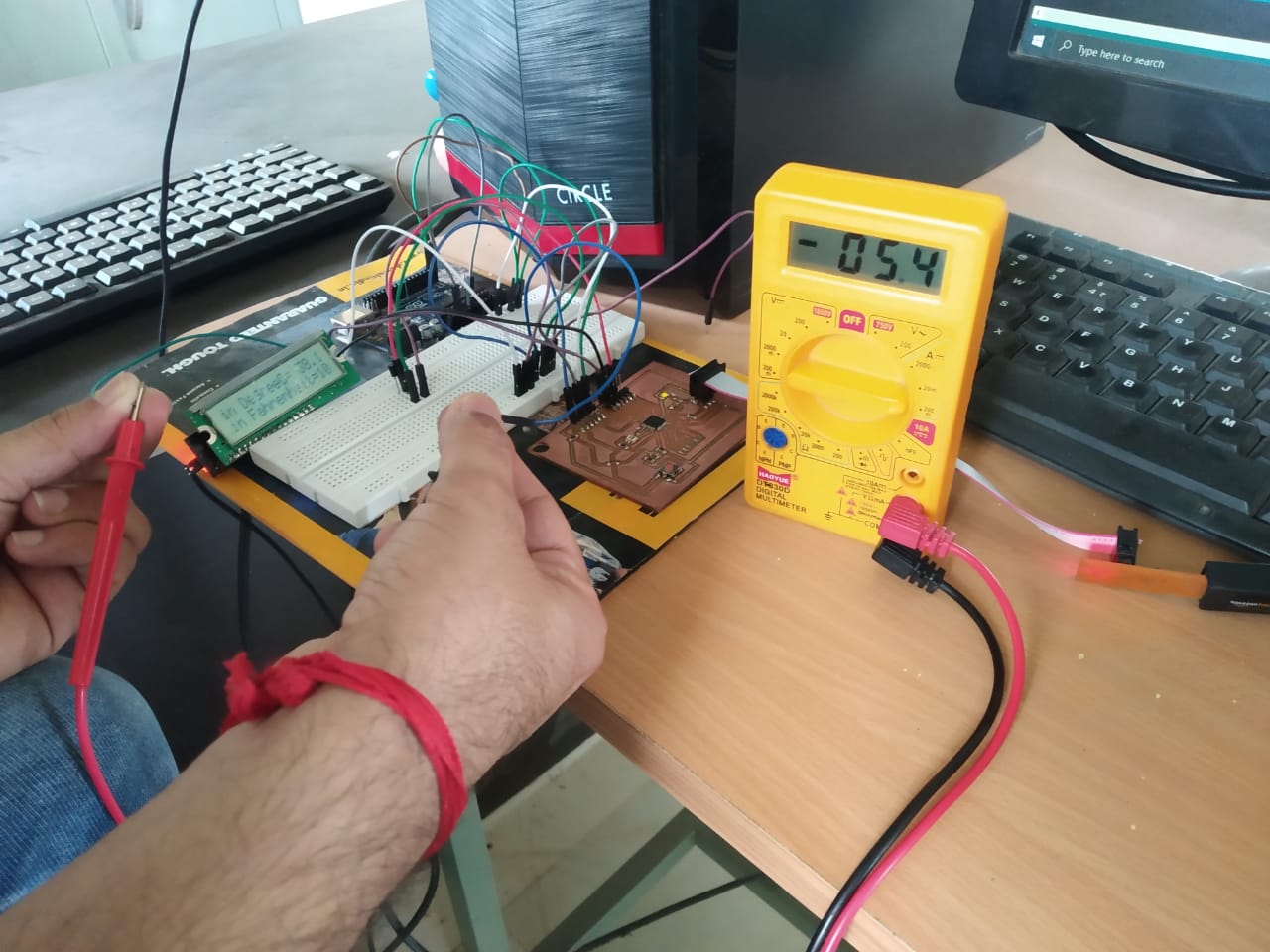
We measured current through the circuit using multimeter.

Power:
In physics, power is the amount of energy transferred or converted per unit time. In the International System of Units, the unit of power is the watt, equal to one joule per second. In older works, power is sometimes called activity. Power is a scalar quantity.
The instantaneous electrical power P delivered to a component is given by P(t)=V(t)xI(t) Where
P(t)= is the instantaneous power, measured in watts (joules per second)
V(t)= is the potential difference (or voltage drop) across the component, measured in volts
I(t)= is the current through it, measured in amperes
So power calculation for LCD is P=VxI, P=5.02x5.04x10^-3
P=25mW
